EKG – Electrocardiography
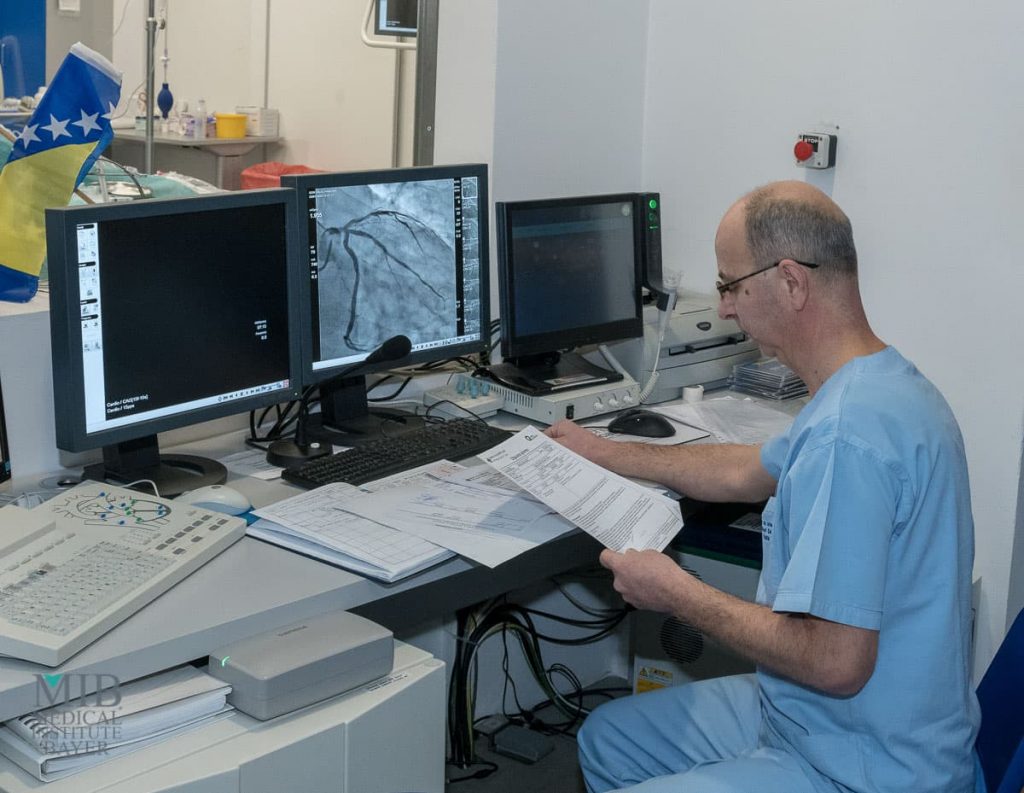

Electrocardiography is the process of recording the electrical activity of the heart over time using electrodes placed on the skin. These electrodes register the electrical changes of the heart muscle during each heart attack. The graphic record of these changes is called an electrocardiogram (ECG).
The heart is a unique muscle in the body that possesses the property of automatic impulse formation and rhythmic contractions. The effect of the electrocardiogram is based on the fact that the heart muscle (myocardium), like any other working muscle, produces electric currents (electrical effect). It is the result of metabolism, biological, chemical and physiological processes in one organism or in a single cell.
This is the most common test performed in cardiology, and a cardiology examination cannot be imagined without it.
An electrocardiogram is a diagnostic test used to detect heart disease. A particular indicator is a change in the function of the heart and the state of the conduction system and heart vessels that feed the heart muscle. The ECG shows the following conditions:
ECG is the gold standard in the diagnosis of cardiac arrhythmias,
It helps in the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction and other forms of coronary disease,
Helps in the diagnosis of electrolyte disorders (e.g. hyperkalemia and hypokalemia)
ECG is used in screening for ischemic heart disease in ergometry,
Expansion and thickening of the heart’s atria and ventricles,
Pericarditis (inflammation of the heart tissue),
Changes in the heart in systemic diseases,
Functioning of the rhythm guide (pacemaker), etc.
ECG can occasionally be useful in non-cardiac diseases such as pulmonary embolism, hypothyroidism, etc.
WORKING HOURS
CONTACTS
- +387 35 309 100
- info@mib.institute
FOR PATIENTS
Zdravstvena ustanova Specijalna bolnica "Medical Institute Bayer" Tuzla već godinama zauzima lidersku poziciju u dijagnostici i tretmanu kardiovaskularnih bolesti u BiH i regionu.
USEFUL LINKS
FOR PATIENTS
Sva prava zadržava MIB

